Plivo Android SDK
The Plivo Android SDK allows developers to create applications capable of making and receiving voice calls in Android apps. The SDK supports Android versions 6.0 and above and Android API level 23 and above.
The current version of the Android SDK is built over the WebRTC framework. It provides high call quality with native WebRTC improvements such as AEC, AGC, and STUN binding requests.
Notes
New changes for the Android SDK
- The new SDK has breaking changes for the method to register an endpoint.
- The SDK is backward compatible.
Terminology
- username: username of an endpoint
- password: password of an endpoint
- token: device token for VoIP push notifications. You can obtain a device token from APNS by registering for push notifications.
- certificateId: certificate ID created in the Plivo console under Voice > Push Credentials — see push credentials documentation.
Here’s an overview of classes and methods available in the SDK.
Register an endpoint
Declare or use user input for the endpoint and password from the console
public final static String PLIVO_USERNAME = "Tatooine";
public final static String PLIVO_PASSWORD = "Jabba";
Instantiate the Endpoint class
- With options
public static HashMap < String, Object > options = new HashMap < String, Object > () {
{
put("debug", true);
put("enableTracking", true);
put("maxAverageBitrate", 21000);
} }; endpoint = Endpoint.newInstance(context, true, this, options);
- Without options
endpoint = Endpoint.newInstance(context, true, this);
Log in with an FCM token after fetching it from Firebase Cloud Messaging
endpoint.login(username, password, fcmToken);
Log in with an FCM token from Firebase and a certificate ID from console
endpoint.login(username, password, fcmToken, certificateId);
Log in without an FCM token
endpoint.login(username, password, regTimeout);
For more information on the login methods, see our documentation on the Endpoint class.
Examples of basic call actions
Make an outbound call
To make an outbound call, use this code.
public final static String PHONE_NUMBER = "12025551111";
Outgoing outgoing = endpoint.createOutgoingCall(); outgoing.call(PHONE_NUMBER);
If you want to include extra headers, use this code instead.
public final static String PHONE_NUMBER = "12025551111";
Map<String, String> extraHeaders = new HashMap<>();
extraHeaders.put("X-PH-Header1", "12345");
extraHeaders.put("X-Ph-Header2", "34567");
outgoing = Phone.getInstance(this).createOutgoingCall();
outgoing.call(PHONE_NUMBER, extraHeaders);
Receive a call
Implement EventListener on your class and override the onIncomingCall method using the command:
public void onIncomingCallConnected(Incoming incoming) { incoming.answer(); }
Autoconnect when the network is available
Configuration parameters
| Attribute | Description | Allowed Values | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| debug | Enable log messages. | true, false | false |
| enableTracking | Set to true if you want to get MediaMetrics events and enable call quality tracking. | true, false | true |
| maxAverageBitrate | Controls your application’s bandwidth consumption for calls. A high maxAverageBitrate value yields better audio quality but may result in more bandwidth consumption. Lowering maxAverageBitrate impacts call quality as the audio is compressed to reduce bandwidth consumption. This parameter applies only to calls using the Opus codec. See RFC-7587 section 7.1 for more info. |
8000 – 48000 | 48000 |
| enableQualityTracking | This parameter can be used to enable and disable two functionalities: MediaMetrics events: enables the client device to display local call issues like broken audio, etc., to the user. Call quality tracking: enables Plivo to capture and display call quality data in Call Insights. When set to all, both MediaMetrics events and call quality tracking are enabled. When set to remoteonly only call quality tracking is enabled. When set to localonly only MediaMetrics events are enabled. When set to none both MediaMetrics events and call quality tracking are disabled. |
CallAndMediaMetrics.ALLCallAndMediaMetrics.NONE CallAndMediaMetrics.REMOTE_ONLY CallAndMediaMetrics.LOCAL_ONLY |
CallAndMediaMetrics.ALL |
Classes and methods
Class: Endpoint
The Endpoint class lets you register a Plivo SIP endpoint, after which you can make and receive calls using it.
private Endpoint endpoint(Context context) {
return endpoint != null ? endpoint : (endpoint = Endpoint.newInstance(context, BuildConfig.DEBUG, this));
Creates the endpoint objects:
public Endpoint(Context context, boolean debug, EventListener eventListener)
- @param context — Application/Activity context.
- @param debug — Setting this to true turns on the Plivo SDK debug logs. Default is false.
- @param eventListener — Login, Call events Callback listener.
Several methods are available in the Endpoint class.
Method: login (String username, String password, String fcmToken, String certificateID)
public boolean login(String username, String password, String fcmToken, String certificateID)
This method registers an endpoint with FCM token and certificate ID. If the endpoint is successfully registered, a notification is sent to the onLogin method of the EventListener. If registration fails, notification is sent to the onLoginFailed method of the EventListener.
- username — The username of the endpoint created on Plivo
- password — The password of the endpoint created on Plivo
- fcmToken — Device token obtained from Firebase. The FCM token is needed to alert the user about incoming calls using Firebase push notifications.
- certificateID — Certificate ID created in the console after uploading push credentials. See our documentation on Setting Up Push Notification.
usage
// retrieve FCM token, then log in FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getInstanceId().addOnSuccessListener(this, instanceIdResult -> { String newToken = instanceIdResult.getToken();
endpoint.login(usernameView.getText().toString(), passwordView.getText().toString(), newToken, certificateID); });
Method: login(String username, String password, String fcmToken)
public boolean login(String username, String password, String fcmToken)
This method registers an endpoint with an FCM token. If the endpoint is successfully registered, a notification is sent to the onLogin method of the EventListener. If registration fails, notification is sent to the onLoginFailed method of the EventListener.
- username — The username of the endpoint created on Plivo
- password — The password of the endpoint created on Plivo
- fcmToken — Device token obtained from Firebase. The FCM token is needed to alert the user about incoming calls using Firebase push notifications.
usage
// retrieve FCM token, then log in FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getInstanceId().addOnSuccessListener(this, instanceIdResult -> { String newToken = instanceIdResult.getToken();
endpoint.login(usernameView.getText().toString(), passwordView.getText().toString(), newToken); });
public setRegTimeout(int timeout)Method: login(String username, String password, int regTimeout)
public boolean login(String username, String password, int regTimeout)
This method registers an endpoint without an FCM token. If the endpoint is successfully registered, a notification is sent to the onLogin method of the EventListener. If registration fails, notification is sent to the onLoginFailed method of the EventListener.
- username — The username of the endpoint created on Plivo
- password — The password of the endpoint created on Plivo
- regTimeout — Seconds to reregister if the app is in the foreground. The allowed value range is 120 to 86,400. The default is 600.
usage
endpoint.login(usernameView.getText().toString(), passwordView.getText().toString(), 600);
```<!-- #### With Access Tokens/ JWT
You can register an endpoint using:
* Access Token, device token, and certificate ID
* Access Token, and device token
* Access Token
* Access Token Generator
For each usage, when the endpoint is successfully registered, the SDK notifies the onLogin of EventListener. In case of a failure, it notifies the onLoginFailed of EventListener.
#### **Method: loginWithJwtToken(String JWTToken)**
```java
public boolean loginWithJwtToken(String JWTToken)
This method registers an endpoint without an FCM token. If the endpoint is successfully registered, a notification is sent to the onLogin method of the EventListener. If registration fails, notification is sent to the onLoginFailed method of the EventListener.
- JWTToken — The JWT you can generate via server-side API or via JWT creator
usage
endpoint.loginWithJwtToken(jwtToken);
Method: loginWithJwtToken(String JWTToken, String deviceToken)
public boolean loginWithJwtToken(String JWTToken, String deviceToken)
This method registers an endpoint with an FCM token. If the endpoint is successfully registered, a notification is sent to the onLogin method of the EventListener. If registration fails, notification is sent to the onLoginFailed method of the EventListener.
- JWTToken — The JWT you can generate via server-side API or via JWT creator.
- deviceToken — Device token obtained from Firebase. The FCM token is needed to alert the user about incoming calls using Firebase push notifications.
Usage
// retrieve FCM token, then log in FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getInstanceId().addOnSuccessListener(this, instanceIdResult -> { String newToken = instanceIdResult.getToken();
endpoint.loginWithJwtToken(jwtToken, newToken);
Method: loginWithJwtToken(String JWTToken, String deviceToken, String certificateId)
public boolean loginWithJwtToken(String JWTToken, String deviceToken, String certificateId)
This method registers an endpoint with an FCM token and certificate ID. If the endpoint is successfully registered, a notification is sent to the onLogin method of the EventListener. If registration fails, notification is sent to the onLoginFailed method of the EventListener.
- JWTToken — The JWT you can generate via server-side API or via JWT creator.
- deviceToken — Device token obtained from Firebase. The FCM token is needed to alert the user about incoming calls using Firebase push notifications.
- certificateId — Certificate ID created in the console after uploading push credentials. See section below on Setting Up Push Notification.
Usage
// retrieve FCM token, then log in FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getInstanceId().addOnSuccessListener(this, instanceIdResult -> { String deviceToken = instanceIdResult.getToken();
endpoint.loginWithJwtToken(jwtToken, deviceToken, certificateID);
Method: loginWithJwtToken(String JWTToken, String deviceToken, String certificateId)
public boolean loginWithAccessTokenGenerator(AccessTokenListener accessTokenListener)
This method enables users to refresh the client-associated JWT Access Token for ongoing authentication. When a token expires the getAccessToken() function of the AccessTokenListener is invoked, the user can implement their own logic for producing the JWT token. If the endpoint is successfully registered, a notification is sent to the onLogin method of the EventListener. If registration fails, notification is sent to the onLoginFailed method of the EventListener.
- AccessTokenListener — This listener consists of an only method getAccessToken(). Implement it if you want to get notified for existing token expiry.
Check out our GitHub example for implementation.
usage
// retrieve FCM token, then log in FirebaseInstanceId.getInstance().getInstanceId().addOnSuccessListener(this, instanceIdResult -> { String deviceToken = instanceIdResult.getToken();
endpoint.loginWithJwtToken(jwtToken, deviceToken, certificateID);
Method: relayVoipPushNotification(Map<String, String> notification)
This method forwards FCM notification data to the Plivo SDK. The onIncomingCall() method is called after calling this function.
When the app is in the killed state and wakes up from the FCM notification, call login(username, password, deviceToken) before calling relayVoipPushNotification(remoteMessage.getData()).
notification - Notification data from FCM.
usage
When receiving a push notification from FCM, check whether the endpoint is logged in. If it’s not, call login(username, password, deviceToken) then call relayVoipPushNotification(remoteMessage.getData()).
@Override public void onMessageReceived(RemoteMessage remoteMessage) {
super.onMessageReceived(remoteMessage);
if (endpoint.login(username, password, deviceToken)) {
endpoint.relayVoipPushNotification(remoteMessage.getData());
}
}
Method: loginForIncomingWithUsername(String username, String password, String certificateId, HashMap<String, String> incomingData)
public boolean loginForIncomingWithUsername(String username, String password, String certificateId, HashMap<String, String> incomingData)
This method forwards FCM notification data to the Plivo SDK. The onIncomingCall() method is called after calling this function.
When the app is in the killed state and wakes up from the FCM notification, no need to call login(username, password, deviceToken) before calling loginForIncomingWithUsername(remoteMessage.getData()).
- username — The username of the endpoint created on Plivo
- password — The password of the endpoint created on Plivo
- certificateID — Certificate ID created in the console after uploading push credentials. See section below on Setting Up Push Notification.
- incomingData — Notification data from FCM.
usage
When receiving a push notification from FCM, no need to check whether the endpoint is logged in.
@Override public void onMessageReceived(RemoteMessage remoteMessage) {
super.onMessageReceived(remoteMessage);
endpoint.loginForIncomingWithUsername(username, password, deviceToken, certificateId, remoteMessage.getData());
}
```<!-- #### **Method: loginForIncomingWithJwt(String deviceToken, String jwtToken, String certificateId, HashMap<String, String> incomingData)**
```java
public boolean loginForIncomingWithJwt(
String token,
String JWTToken,
String certificateId,
HashMap < String, String > incomingData)
This method forwards FCM notification data to the Plivo SDK. The onIncomingCall() method is called after calling this function.
When the app is in the killed state and wakes up from the FCM notification, no need to call login(JWTToken, deviceToken) before calling loginForIncomingWithJwt(remoteMessage.getData()).
- token — Device token obtained from Firebase. The FCM token is needed to alert the user about incoming calls using Firebase push notifications.
- JWTToken — The JWT you can generate via server-side API or via JWT creator.
- certificateID — Certificate ID created in the console after uploading push credentials. See section below on Setting Up Push Notification.
- incomingData — Notification data from FCM.
usage
When receiving a push notification from FCM, no need to check whether the endpoint is logged in.
@Override public void onMessageReceived(RemoteMessage remoteMessage) {
super.onMessageReceived(remoteMessage);
endpoint.loginForIncomingWithJwt(deviceToken, JWTToken, deviceToken, certificateId, remoteMessage.getData());
}
``` -->
#### **Method: logout**
This method unregisters an endpoint.
##### **usage**
```java
endpoint.logout();
Method: createOutgoingCall
Calling this method returns an Outgoing object linked to the registered endpoint that can be used to make outbound calls. Calling this method on an unregistered PlivoEndpoint object returns null.
public Outgoing createOutgoingCall()
public void getOutgoingCall() {
Outgoing outgoing = endpoint.createOutgoingCall();
return outgoing;
}
usage
Method: submitCallQualityFeedback
public void submitCallQualityFeedback(
String callUUID,
Integer starRating,
ArrayList < String > issueList,
String comments,
Boolean sendConsoleLogs,
FeedbackCallback callback)
This method submits call quality feedback after an end, reject, decline, or any other event of an outgoing or incoming call. If the feedback is successfully submitted, the onSuccess callback is called. If there’s an input validation error, the onValidationFail callback is called. If the feedback submission fails, the onFailure callback is called.
All three callbacks are implementations of the endpoint.FeedbackCallback interface.
-
callUUID — Mandatory string parameter used to identify the call the feedback belongs to. You can get the callUUID for the last call using getLastCallUUID().
-
starRating — Mandatory integer parameter with a value from 1 to 5. For a score from 1 to 4, the
issues parameter is mandatory; for a score of 5 it’s optional.
-
issueList — IssueList is an array and must have at least one of these reasons for a starRating value from 1 to 4 — AUDIO_LAG, BROKEN_AUDIO, CALL_DROPPPED, CALLERID_ISSUES, DIGITS_NOT_CAPTURED, ECHO, HIGH_CONNECT_TIME, LOW_AUDIO_LEVEL, ONE_WAY_AUDIO, ROBOTIC_AUDIO, OTHERS
-
Comments — Optional string attribute for users remarks; maximum length 280 characters.
-
sendConsoleLogs — Optional boolean parameter with default value false. Set to true to let Plivo’s team collect and analyze Android SDK logs for a better understanding of an issue.
-
callback — This is the FeedbackCallback instance that accesses the onFailure, onSuccess, and onValidationFail callback methods.
usage
endpoint.submitCallQualityFeedback(callUUID, starRating, issueList, comments, sendConsoleLogs, new FeedbackCallback() {
@Override public void onFailure(int statuscode) {
Log._i_(_TAG_, "Status code : " + Integer._toString_(statuscode));
}
@Override public void onSuccess(String response) {
Log._i_(_TAG_, "Success " + response);
}
@Override public void onValidationFail(String validationErrorMessage) {
Log._i_(_TAG_, "Validation Failed : " + validationErrorMessage);
}
});
Method: getCallUUID
public String getCallUUID();
Returns a string call UUID if a call is active, else returns null.
usage
String callUUID = endpoint.getCallUUID();
Class: Outgoing
The Outgoing class contains methods to make and control an outbound call.
import com.plivo.endpoint.Outgoing;
public Outgoing outgoing;
outgoing = new Outgoing(endpoint);
These are the methods available in the Outgoing class.
Method: call
public boolean call(String dest)
Use the Call method to make an outbound call. Use the SIP URI or a number to make a call.
usage
outgoing = Phone.getInstance(this).createOutgoingCall(); outgoing.call(phoneNumberTepublic boolean call(String dest)
Method: mute
public boolean mute()
Calling this method on the Outgoing object mutes the call.
usage
if(outgoing!=null) {
outgoing.mute();
}
Method: unmute
public boolean unmute()
Calling this method on the Outgoing object unmutes the call.
usage
if(outgoing!=null) {
outgoing.unmute();
}
Method: sendDigits
public boolean sendDigits(String digit)
Calling this method on the Outgoing object with digits sends DTMF (0-9, *, and #) on the call.
usage
if(outgoing!=null) { outgoing.sendDigits(dtmfText.getText().toString()); }
Method: hangup
public void hangup()
Calling this method on the Outgoing object disconnects the call.
usage
outgoing.hangup();
Class: Incoming
The Incoming class contains methods to handle an incoming call. The public void onIncomingCall(Incoming incoming) eventListener receives an object of this class.
These are the methods available in the Incoming class.
Method: answer
public void answer()
This method answers an incoming call.
usage
if (incoming != null) { incoming.answer(); }
Method: mute
public boolean mute()
This method mutes the call.
usage
if (incoming != null) { incoming.mute(); }
Method: unmute
public boolean unmute()
This method unmutes the call. Calling this method on an already unmuted call has no effect.
usage
if (incoming != null) { incoming.unmute(); }
Method: sendDigits
public boolean sendDigits(String digit)
Using this method on the Incoming object with digits sends DTMF (0-9, *, and #) on that call.
usage
if (incoming != null) { incoming.sendDigits(dtmfText.getText().toString()); }
Method: hangup
public void hangup()
This method disconnects an incoming call.
usage
incoming.hangup();
Method: reject
public void reject()
This method rejects an incoming call.
usage
incoming.reject();
Class: EventListener
These are the methods available in the EventListener class.
Method: onLogin
public void onLogin()
This method is called when registration to an endpoint is successful.
usage
@Override
public void onLogin() {
notifyLogin(true);
// notified that login is success and can proceed to other screens.
}
Method: onLoginFailed
public void onLoginFailed()
This method is called when registration to an endpoint fails.
usage
@Override
public void onLoginFailed() {
notifyLogin(false);
}
```<!-- ### **Method: onLoginFailed** for JWT
```java
public void onLoginFailed(String message)
This method is called when registration via JWT to an endpoint fails.
Possible error events:
INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN, INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN_HEADER, INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN_ISSUER, INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN_SUBJECT, ACCESS_TOKEN_NOT_VALID_YET, ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRED, INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN_SIGNATURE, INVALID_ACCESS_TOKEN_GRANTS, EXPIRATION_EXCEEDS_MAX_ALLOWED_TIME, MAX_ALLOWED_LOGIN_REACHED
usage
@Override
public void onLoginFailed(String message) {
Log.d(TAG,message);
}
``` --><!-- ### **Method: onPermissionDenied**
```java
public void onPermissionDenied(String message)
This method is called when the user logs in with JWT and does have the permission to make outgoing/receive incoming calls.
usage
@Override
public void onPermissionDenied(String message) {
Log.d(TAG,message);
}
``` -->
#### **Method: onIncomingCall**
```java
public void onIncomingCall(Incoming incoming)
When a call comes in to a registered endpoint, this method receives an Incoming object.
usage
@Override
public void onIncomingCall(Incoming incoming) {
// create call obj Call inCall = new Call.Builder()
.setId(incoming.getCallId())
.setType(Call.TYPE.INCOMING)
.setState(Call.STATE.RINGING) .setContact(contactUtils.getContact(from(incoming.getFromContact(), incoming.getFromSip()))) .setData(incoming)
.build();
addToCallStack(inCall);
handler.postDelayed(ringingTimeoutRunnable, Call.CALL_RINGING_TIMEOUT);
}
Method: onIncomingCallConnected
public void onIncomingCallConnected(Incoming incoming)
On an incoming call, if the call is connected by the caller, this method is triggered by the Incoming method.
Method: onIncomingCallRejected
public void onIncomingCallRejected(Incoming incoming)
On an incoming call, if the call is rejected by the caller, this method is triggered by the Incoming object.
usage
@Override
public void onIncomingCallRejected(Incoming incoming) {
Call call = getCall(incoming.getCallId());
if (call != null) { call.setState(Call.STATE.REJECTED);
removeFromCallStack(call);
}
handler.removeCallbacks(ringingTimeoutRunnable);
}
Method: onIncomingCallHangup
public void onIncomingCallHangup(Incoming incoming)
On an incoming call, if the call is disconnected by the caller after being answered, this method is triggered by the Incoming object.
usage
@Override
public void onIncomingCallHangup(Incoming incoming) {
Call call = getCall(incoming.getCallId());
if (call != null) { call.setState(Call.STATE.HANGUP);}}
Method: onIncomingDigitNotification
public void onIncomingDigitNotification(String digits)
This method is called with the digits received on a call.
usage
@Override public void onIncomingDigitNotification(String digit) {}
Method: onOutgoingCall
public void onOutgoingCall(Outgoing outgoing)
This method is called when an outgoing call is in progress before the ringing state.
usage
@Override public void onOutgoingCall(Outgoing outgoing) {}
Method: onOutgoingRinging
public void onOutgoingRinging(Outgoing outgoing)
This method is called when an outgoing call is ringing.
usage
@Override public void onOutgoingCallRinging(Outgoing outgoing) {}
Method: onOutgoingCallAnswered
public void onOutgoingCallAnswered(Outgoing outgoing)
This method is called when an outgoing call is answered.
usage
@Override public void onOutgoingCallAnswered(Outgoing outgoing) {}
Method: onOutgoingCallHangup
public void onOutgoingCallHangup(Outgoing outgoing);
This method is called when an outgoing call is disconnected by the called number after the call was answered.
usage
@Override public void onOutgoingCallHangup(Outgoing outgoing) {}
Method: onOutgoingCallRejected
public void onOutgoingCallRejected(Outgoing outgoing);
This method is called when an outgoing call is rejected by the called number.
usage
@Override public void onOutgoingCallRejected(Outgoing outgoing) {}
Method: mediaMetrics
For an ongoing call, if any of the below events are triggered, the MediaMetrics listener will be called with the values of the event in the mediaMetrics object. To enable this feature, set the enableTracking flag to true during endpoint initialization.
MediaMetrics Events
| Events | Description | Example |
| high_jitter | When jitter is higher than 30 milliseconds for two out of the last three samples. This event is generated individually for the local stream and remote stream. | { group: 'network', level: 'warning', type: 'high_jitter', active: true/false, // false when the value goes to normal level (two out of last three samples have jitter less than 30 ms) value: '<average jitter value>', desc: 'high jitter detected due to network congestion, can result in audio quality problems', stream: 'local || remote' } |
| high_rtt | When round-trip time (RTT) is higher than 400 milliseconds for two out of the last three samples. | { group: 'network', level: 'warning', type: 'high_rtt', active: true/false, // false when value goes to normal level (two out of last three samples have RTT less than 400 ms) value: '<average rtt value>', desc: 'high latency detected, can result in delay in audio', stream: 'None' } |
| high_packetloss | When the packet loss is > 10%. This event is generated individually for the local stream and remote stream. | { group: 'network', level: 'warning', type: 'high_packetloss', active: true/false, // false when value goes to normal level value: '<average packet loss value>', desc: 'high packet loss is detected on media stream, can result in choppy audio or dropped call', stream: 'local || remote' } |
| low_mos | When sampled mean opinion score (MOS) is < 3.5 for two out of the last three samples. | { group: 'network', level: 'warning', type: 'low_mos', active: true/false, // false when value goes to normal level. value: '<current_mos_value>', desc: 'low Mean Opinion Score (MOS)', stream: 'None' } |
| no_audio_received | When remote or local audio is silent. This event is generated individually for the local stream and remote stream. | { group: 'audio', level: 'warning', type: 'no_audio_received', active: true/false, // false when value goes to normal level value: '<current_value_in_dB>', desc: 'no audio packets received' stream: 'local || remote' } |
Setting up push notification
This section explains how to receive incoming calls on the Plivo Android SDK using Firebase. To receive an incoming call, you must:
- Create a project on Firebase.
- Register your app on Firebase.
- Add the Firebase config file and Firebase SDK into your app.
- Copy the Firebase service accounts token to the Plivo Dashoboard.
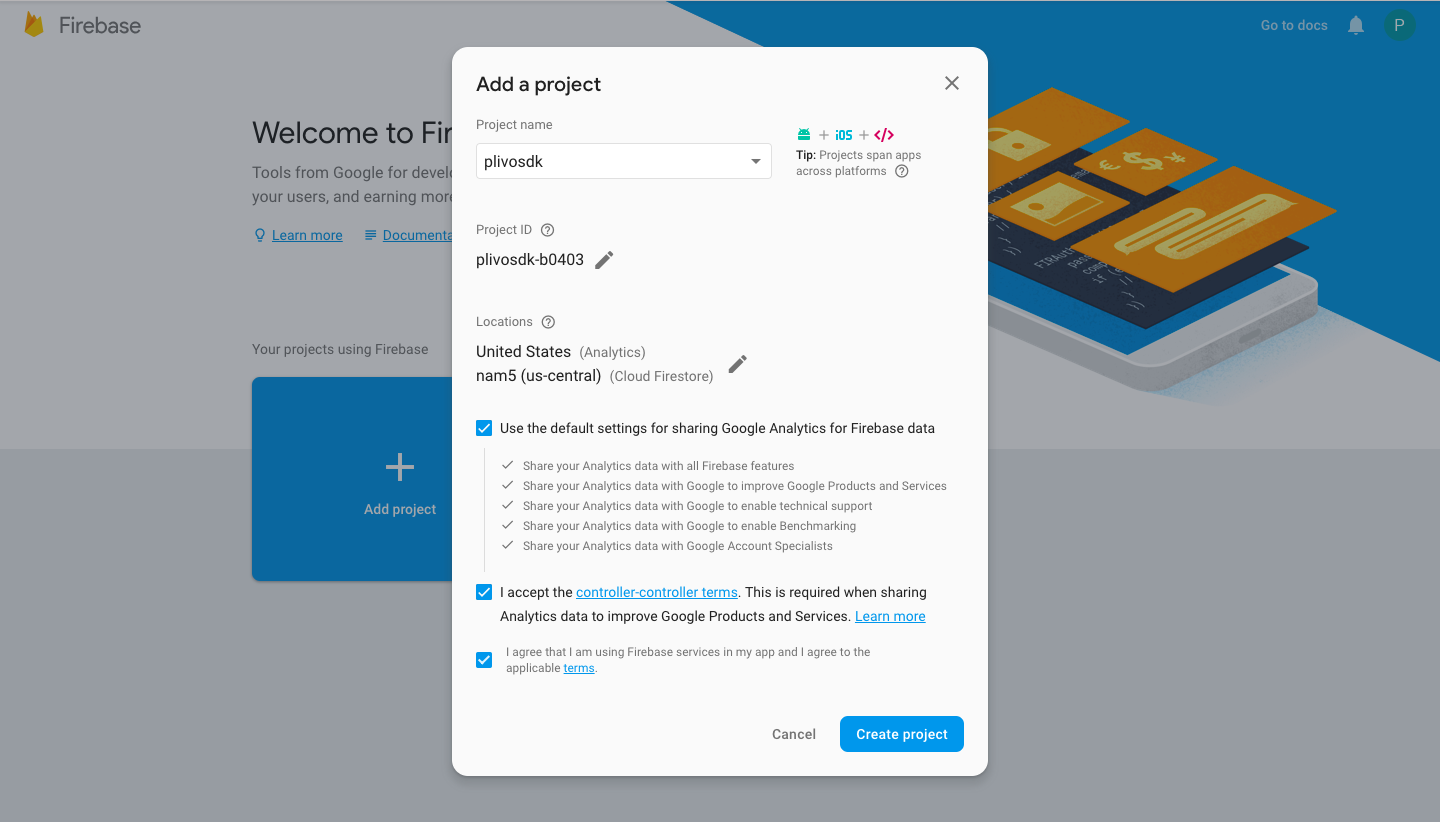
Create a project on Firebase
On the Firebase console, click Add project. Specify a project name and click Create project.
Register your app on Firebase
Go to the Android section of your project home page and register your Android package on Firebase.
Click Register app.
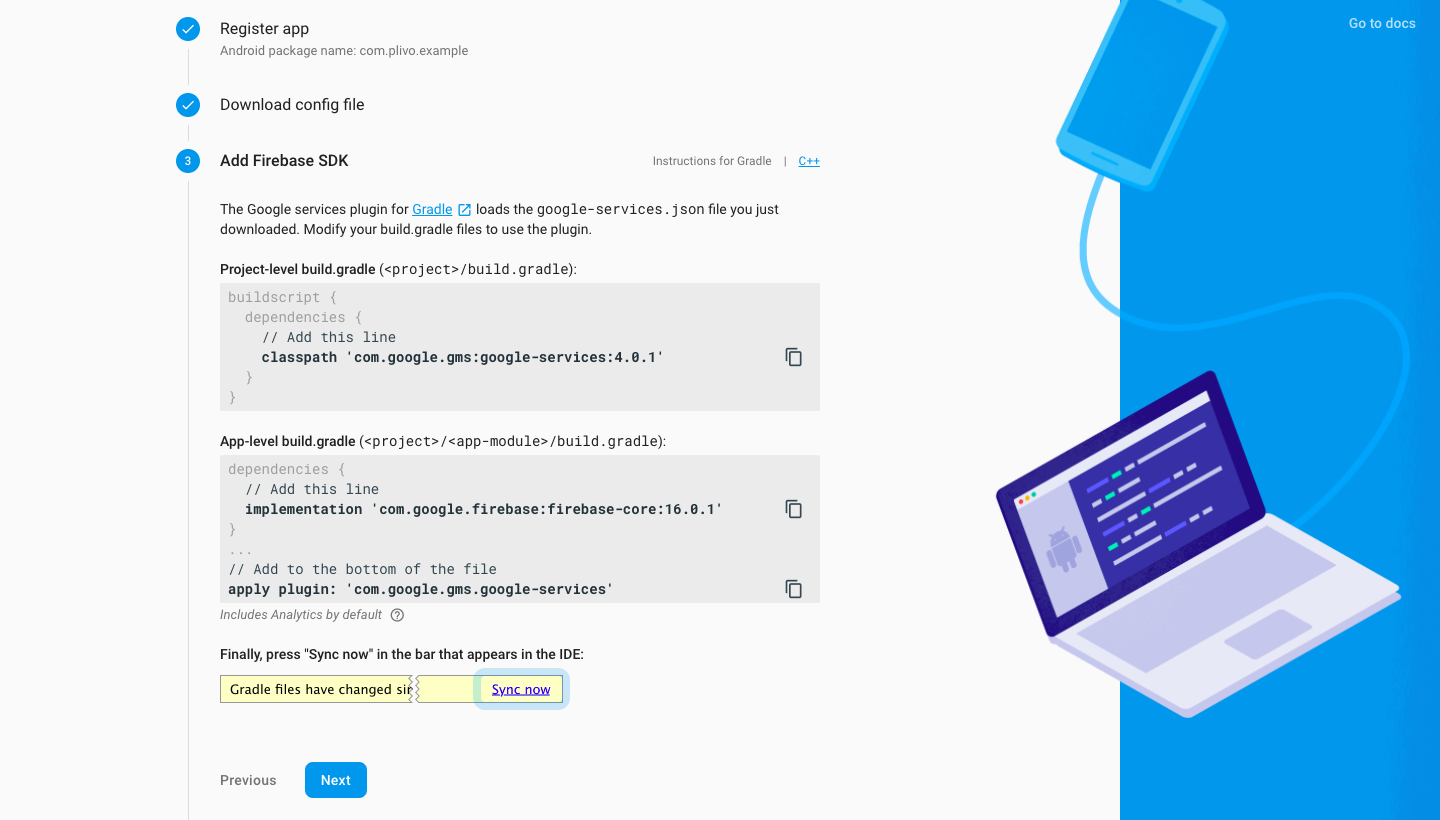
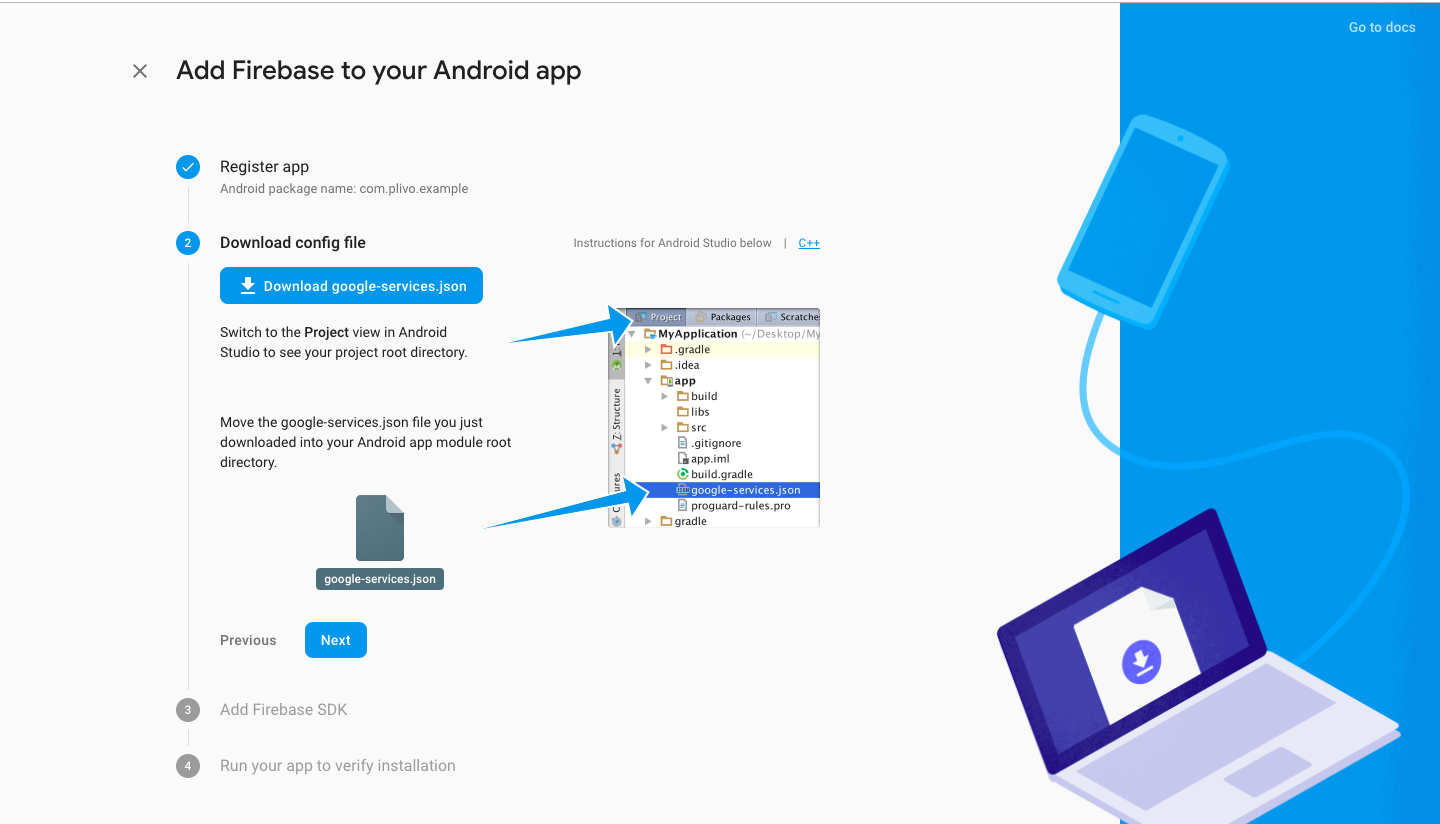
Add the Firebase config file and SDK into your app
Download the Firebase google-services.json file.

Move it into your Android app module root directory, then click Next.
Make the required changes to the Gradle of your Android app as instructed.
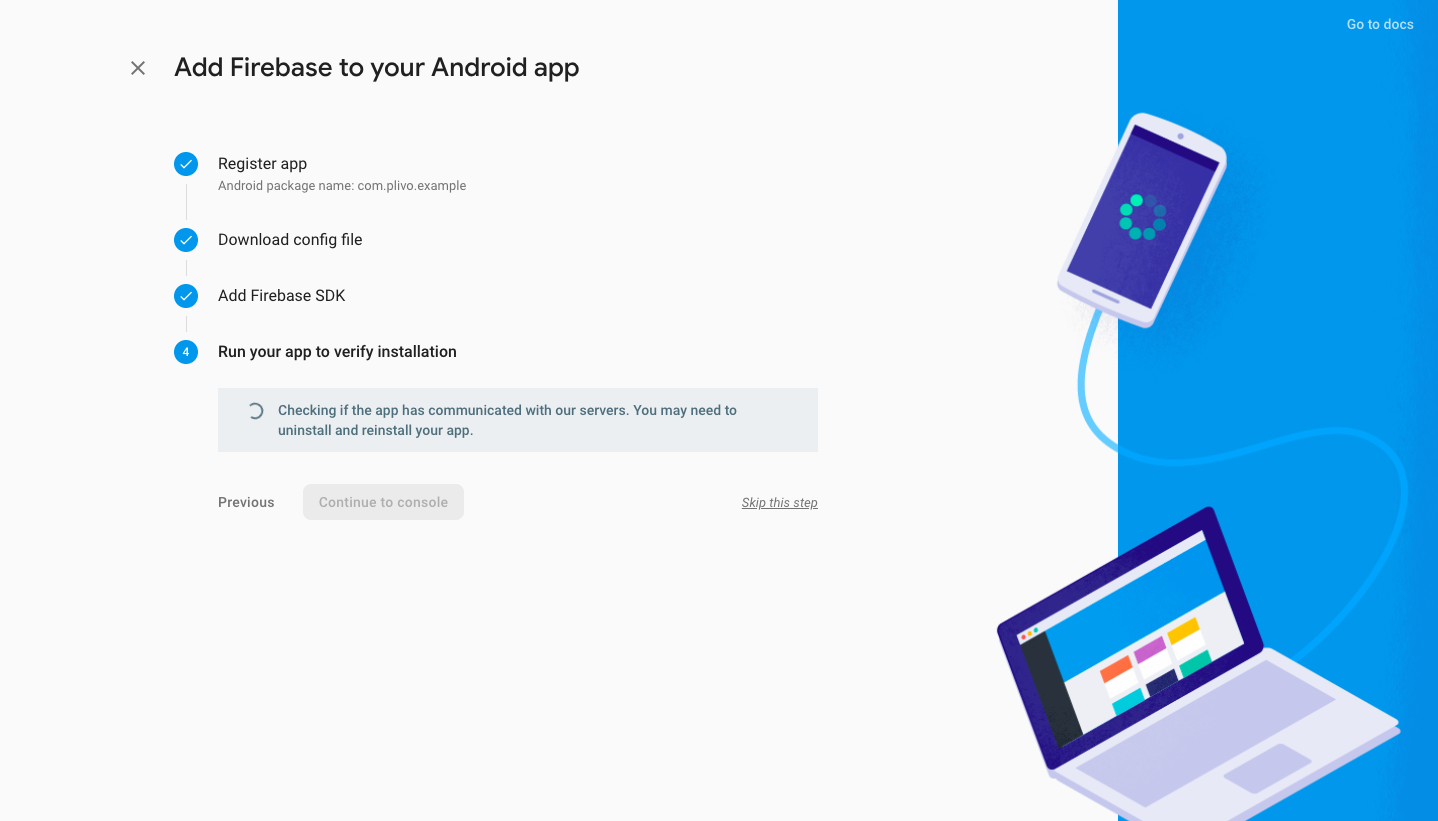
Wait for verification to be completed, then continue to the console.
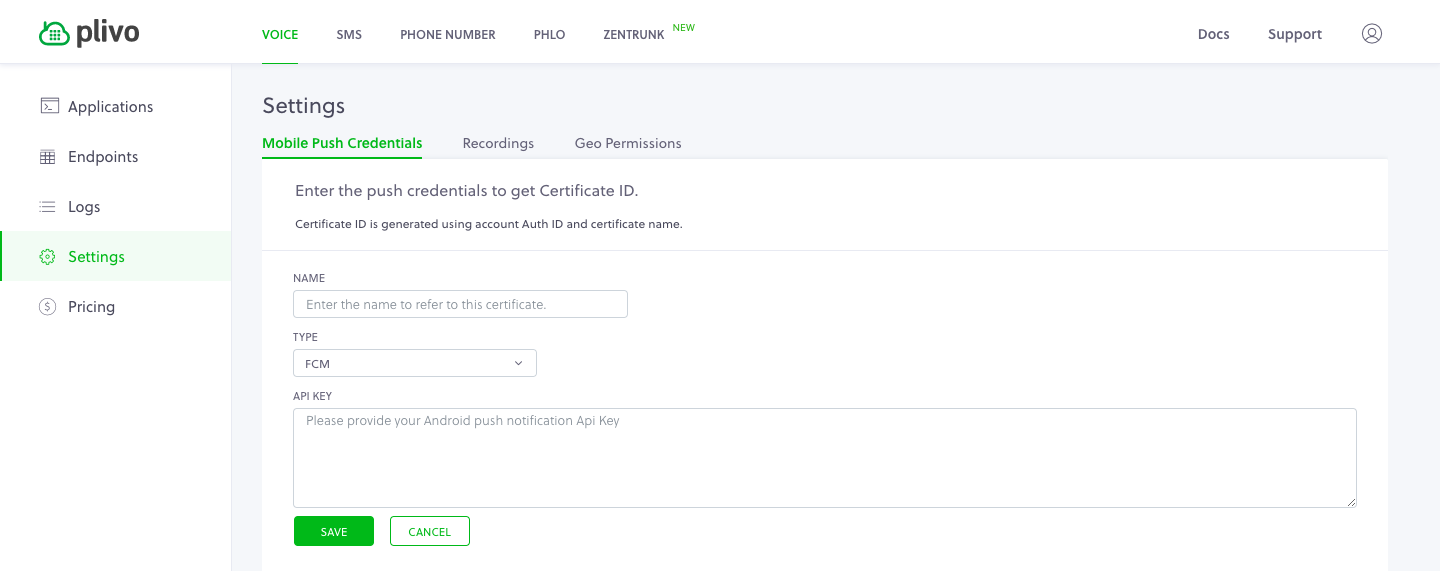
Copy the Firebase service accounts token to the Plivo Dashoboard
From the project settings, under the Service accounts tab, download the private key and copy the token.

Go to Voice > Mobile Push Credentials on the Plivo console and click Update New Push Credential. Give the credential a name and select FCM as the type. Paste the server key token into the API Key box, then click Save.
Resources
FAQ
- Where can I see an example app that shows how to use the Android SDK to make calls?
- The PlivoSimpleQuickStart app shows how to use the Android SDK with minimum code.
- How can I file support tickets or report issues? Create a ticket on our support portal. Include the details below to help us debug issues quickly.
- Description of your use case (app backgrounded, on Wi-Fi/mobile data, lot of network fluctuations)
- Plivo SDK Verbose Logs (Android application logs)
- Plivo will look for logcat logs that starts with “D/PlivoEndpoint” or “E/PlivoEndpoint”
-
All SIP transactions, such as
SIP/2.0 100 Trying Via: SIP/2.0/TLS 52.9.254.127:5061;received=52.9.254.127;branch=z9hG4bKc497.8ec67418aa83e5d7d0f48ad11f78026c.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 52.220.63.151:5080;rport=5080;received=52.220.63.151;branch=z9hG4bKKK6pv4Farvy9m Record-Route: <sip:52.9.254.127:5061;transport=tls;lr;r2=on;ftag=NN36BrBcQ48pK;did=8c6.4611> Record-Route: <sip:52.9.254.127;lr;r2=on;ftag=NN36BrBcQ48pK;did=8c6.4611> Call-ID: 62b89520-3410-11e9-90de-d1c5e59c76a4 From: "android2181024115535" <sip:+654321@52.220.63.151>;tag=NN36BrBcQ48pKTo: <sip:android1181024115518@52.9.254.127> CSeq: 725237 INVITE Content-Length: 0
- Plivo callUUID (for instance, Call-ID:352231d3-3ea9-40c8-8259-e4843f5b02fc)
- Plivo SDK version
- Plivo SDK methods call flows, such as:
- endpoint.login();
- outgoing.callH(num, headers);
- Android device version (for instance, Android 12.1.0_r11)
- Android device model (for example, Samsung Galaxy S22 Plus)
Best practices
- Don’t use deprecated methods, because they will be prone to crashes and NoMethodError when removed in the future.
- Use the deviceToken while logging in to get an incoming call via push notification instead of using the background service to run forever in the background and watch for incoming calls.
